Barcode vs. RFID: Key Differences and Their Impact on Modern Technology
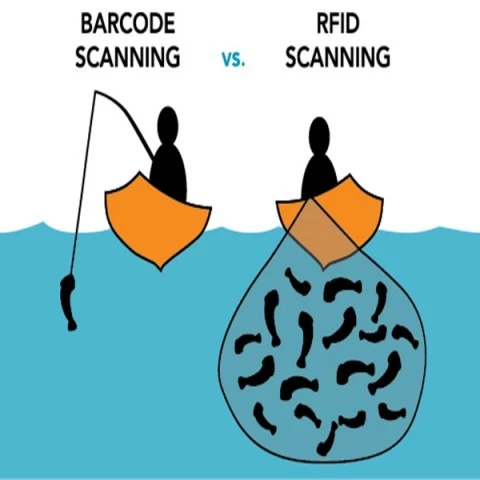
In today’s fast-paced world, efficient tracking and identification systems are crucial for industries ranging from retail to logistics. Two of the most widely used technologies for this purpose are barcodes and Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID). While both serve similar functions, they differ significantly in operation, efficiency, and application.
How Barcodes Work
Barcodes are visual representations of data that require a direct line of sight to be scanned by a laser or optical reader. They are cost-effective, easy to implement, and have been the standard for decades in retail and inventory management. However, their limitations include the need for close proximity and manual scanning, which can slow down processes.
How RFID Works
RFID, on the other hand, uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Unlike barcodes, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning—tags can be read from a distance and even through obstacles. This enables faster, bulk scanning, making RFID ideal for supply chain management, asset tracking, and contactless payment systems. However, RFID systems are more expensive and complex to deploy than barcodes.
Key Differences
-
Scanning Method: Barcodes need direct visibility; RFID does not.
-
Data Capacity: RFID tags can store more information than barcodes.
-
Durability: RFID tags are more resistant to environmental damage.
-
Cost: Barcodes are cheaper, while RFID offers advanced automation.
The Future of Tracking Technology
As industries demand faster and smarter solutions, RFID is gaining traction in sectors like healthcare, warehousing, and smart retail. However, barcodes remain relevant due to their simplicity and low cost. The choice between the two depends on specific business needs—balancing efficiency, scalability, and budget.
Experts predict that hybrid systems combining both technologies may emerge, leveraging the strengths of each to optimize tracking and data management in the digital age.



