RFID Technology: What It Is and How It Works
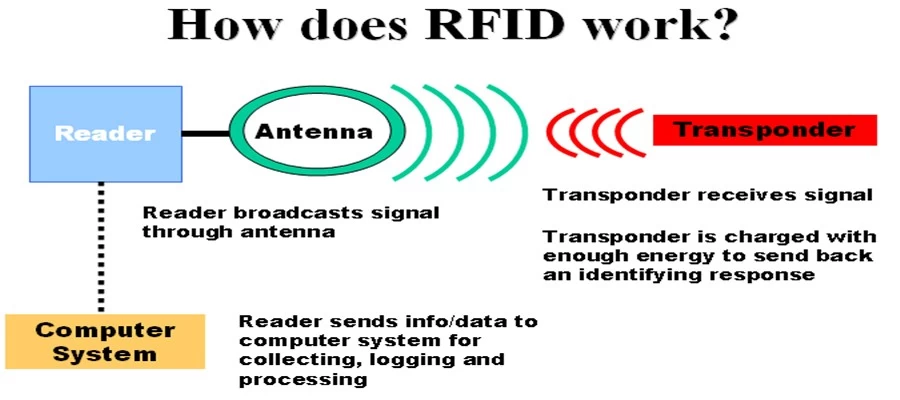
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Widely used in retail, logistics, healthcare, and security, RFID has revolutionized inventory management, asset tracking, and contactless payments.
How Does RFID Work?
An RFID system consists of three key components:
-
RFID Tags – Small electronic devices containing a microchip and antenna that store and transmit data.
-
RFID Reader – A device that sends and receives radio signals to communicate with the tags.
-
Backend Database – A system that processes and stores the collected information.
When an RFID tag comes within range of a reader, the reader emits a radio signal that powers the tag (in passive systems) or activates it (in active systems). The tag then sends back stored data, such as a unique identification number, which the reader forwards to a database for processing.
Applications of RFID
-
Retail & Supply Chain – Enables real-time inventory tracking, reducing losses and improving efficiency.
-
Healthcare – Tracks medical equipment and patient records securely.
-
Access Control – Used in keycards for buildings and events.
-
Contactless Payments – Powers tap-to-pay cards and mobile wallets.
With advancements in IoT and AI, RFID continues to evolve, offering smarter, faster, and more secure tracking solutions across industries.
Stay tuned for more updates on emerging technologies!



