Understanding RFID Systems: Key Components, How They Work, and Real-World Uses
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has transformed industries by enabling wireless tracking and data collection. But how do RFID systems actually function, and what makes them so valuable across different sectors? Let’s break down their components, working principles, and practical applications.
How RFID Systems Work
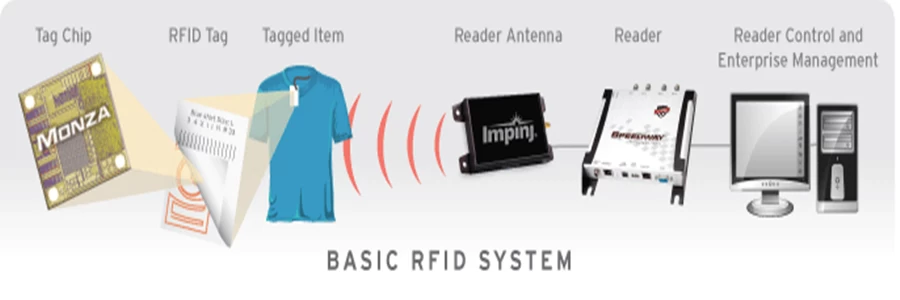
RFID systems use electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Unlike barcodes, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning, allowing faster and more efficient data capture. The system operates in three simple steps:
-
The RFID reader emits a radio signal.
-
The RFID tag (attached to an object) receives the signal and responds with stored data.
-
The reader collects this information and sends it to a central database for processing.
Main Components of an RFID System
-
RFID Tags – These contain a microchip and antenna. They can be:
-
Passive (no battery, powered by the reader’s signal)
-
Active (battery-powered for longer range)
-
Semi-passive (battery-assisted but only transmits when activated)
-
-
RFID Readers – Devices that send and receive signals from tags. They can be handheld, fixed, or integrated into other systems.
-
Antennas – Boost signal strength between tags and readers.
-
Software & Database – Processes and stores the collected data for real-time tracking and analytics.
Where Are RFID Systems Used?
-
Retail & Inventory Management – Stores use RFID to prevent theft and automate stock checks.
-
Logistics & Supply Chain – Companies track shipments globally with RFID-enabled labels.
-
Healthcare – Hospitals manage equipment, patient wristbands, and medication tracking.
-
Access Control & Security – RFID cards replace traditional keys in offices and hotels.
-
Smart Agriculture – Farmers monitor livestock and manage supply chains efficiently.
The Future of RFID
With advancements in IoT and AI, RFID systems are becoming smarter, enabling predictive analytics and automation in smart cities, manufacturing, and beyond.
As businesses seek efficiency and real-time data, RFID technology continues to expand—making it a critical tool in our connected world.
Would you like to know how RFID compares to NFC or Bluetooth tracking? Let us know in the comments!



