RFID vs. NFC: Key Differences in Working Methods and Requirements
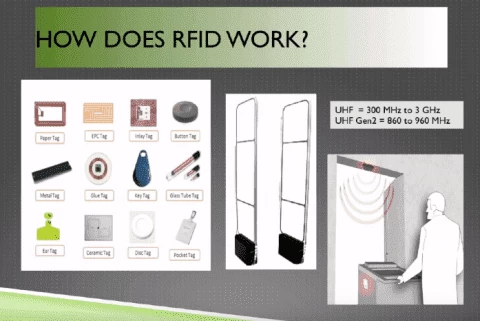
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near Field Communication (NFC) are both wireless technologies, but they operate differently and serve distinct purposes. RFID is designed for long-range tracking, often used in logistics and inventory management, while NFC enables short-range, secure data exchange, commonly found in contactless payments and smart devices.
RFID systems typically require a reader and passive tags, functioning over distances up to several meters. In contrast, NFC operates within a 4 cm range, ensuring secure transactions and two-way communication. Additionally, NFC devices can act as both readers and tags, unlike most RFID setups.
Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses choosing the right technology for their needs. While RFID excels in asset tracking, NFC is ideal for secure, close-proximity interactions. Both have unique advantages, shaping the future of wireless connectivity.



